
The following steps describe how to create mirrored disks on UEFI volume. To restore data to the UEFI partition, the master server should be UEFI partitioned.Įxample 5: Creating Mirrored system volume and boot volume. Note: You only need to retain the boot volume.
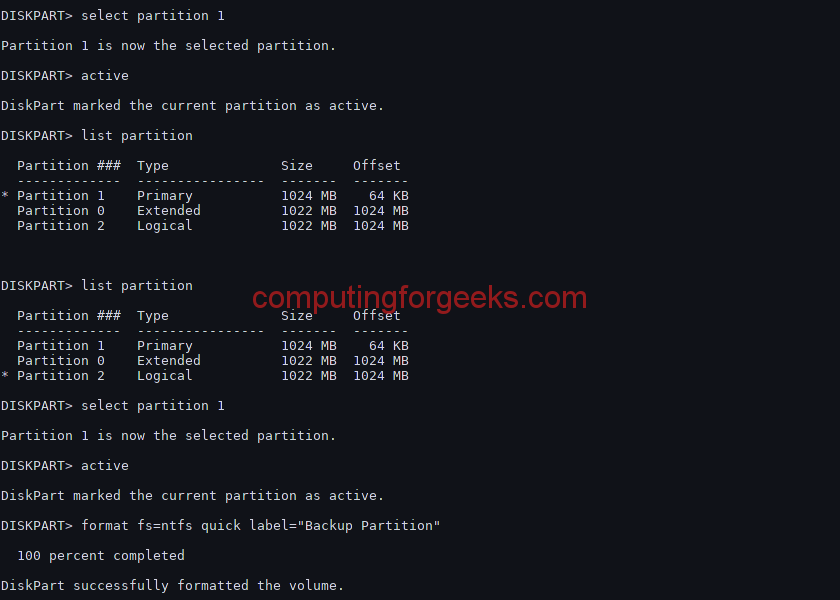
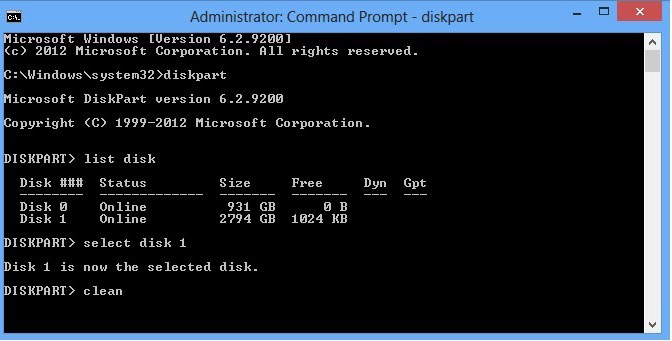
(Optional) Format the system volume to FAT32. To create UEFI partition, disks must be converted to GPT type first. Select disks and convert to the GPT type. Similarly, you can create simple, stripe, or other dynamic disk types.Įxample 4: Creating UEFI system volume and boot volume Select disks and convert to a Dynamic storage type.Ĭonvert each disk except Disk 0 to dynamic disks. You do not need to run the retain command.Įxample 3: Creating a non-system/boot disk volume using the DiskPart command. Note: If you created a UEFI System partition, format it to a FAT32 file system before you can restore data. (Optional) Assign the volume to a drive letter and format it. (Optional) Mark the system partition as active. Create simple dynamic volumes for the System and Boot volume. (Optional) Convert to GPT style if needed. Select a disk, whether it is Raw or Basic disk, and convert it to a dynamic storage type.Ĭreate the boot and system volume on disk 0. (Optional) Assign the volume a drive letter and format it.Įxample 2: Creating a System and a Boot dynamic volume using the DiskPart command. Note: Use active command only for the system partition. Create basic volumes for the System and Boot volume.ĭISKPART>create partition primary size=100. (Optional) Convert to GPT style, if needed Select a disk, whether it is Raw or dynamic disk, and convert it to basic storage type.Ĭreate the boot and system volume on disk 0. Example 1: Creating basic disks using the DiskPart command. The following examples show how to create basic and dynamic disks using the DiskPart command. 
Creating Disks and Volumes Using the DiskPart Command







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
